How are humans protected from solar radiation?
The Sun gives off rays of light that we can see. There is a range of wavelengths that is visible to the human eye. These wavelengths represent a small part of the full spectrum of light.
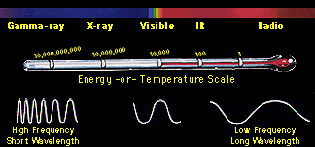 Very short light waves are called x-rays. You may have also heard of something called ultraviolet radiation (ultraviolet is called "UV" for short). Ultraviolet rays are damaging to life forms, and X-rays are even more dangerous in great amounts. The Sun gives off many rays of light that we cannot see that could potentially harm us. So why are we still alive? Earth's atmosphere prevents most UV and X-rays from reaching earth.
Very short light waves are called x-rays. You may have also heard of something called ultraviolet radiation (ultraviolet is called "UV" for short). Ultraviolet rays are damaging to life forms, and X-rays are even more dangerous in great amounts. The Sun gives off many rays of light that we cannot see that could potentially harm us. So why are we still alive? Earth's atmosphere prevents most UV and X-rays from reaching earth.
 |
|
Still, animals and people who live at high altitudes where the Earth's atmosphere is thinner are vulnerable to the damaging effects of the Sun. |
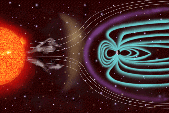 Earth's magnetic field deflects particles emitted by the Sun. But when astronauts and satellites are launched into space beyond Earth's protective barriers, they are vulnerable to to many types of rays and particles emitted by the Sun during solar events. So scientists are studying the Sun in order to be able to predict when changes in the Sun might occur, and perhaps even how to counter their effects.
Earth's magnetic field deflects particles emitted by the Sun. But when astronauts and satellites are launched into space beyond Earth's protective barriers, they are vulnerable to to many types of rays and particles emitted by the Sun during solar events. So scientists are studying the Sun in order to be able to predict when changes in the Sun might occur, and perhaps even how to counter their effects.